At present, domestic and foreign researchers have designed a variety of WSN-oriented routing protocols, which are divided into four categories: data-centric, hierarchical, location-based, based on data flow model and quality of service (QoS) requirements.
(1) Data-centric routing protocol
This type of routing protocol is based on query and target data naming, which reduces redundant data transmission through data fusion.
â‘ Flooding protocol and Gossiping protocol: These are the two most classic and simple traditional network routing protocols. In the Flooding protocol, nodes generate or receive data and broadcast it to all neighboring nodes. Data packets will not stop propagating until they expire or reach their destinations. The protocol has serious flaws: implosiON, a node receives multiple copies of the same data from neighboring nodes at the same time; overlap, the node receives successively the same data sent by multiple nodes monitoring the same area; resources With blindness (resource blindness), a node forwards data in any case regardless of its own resource constraints. The Gossiping protocol is an improvement to the Flooding protocol. The nodes will randomly forward the data generated or received to avoid implosion, but increase the delay. These two protocols do not need to maintain routing information, nor do they need any algorithms. They are simple but have poor scalability.
②SPIN protocol: SPIN (sensor protocols for inf ° rmatlon vla negoTIaTIon) protocol node uses three messages to communicate: data description ADV, data request REQ and data DATA. The protocol names the data with abstract metadata, and there is no uniform standard for the naming method. After the node generates or receives the data, it uses the ADV message containing metadata to notify the neighboring node. The neighboring node that needs the data makes a request with the REQ message, and then sends the DATA message to the requesting node. The advantage of this protocol is that the ADV message reduces the implosion problem; the overlapping problem is solved by data naming; the node decides whether to conduct ADV notification based on its own resources and application information, avoiding the blind problem of resource utilization; with the Flooding protocol and Gossiping protocol
In comparison, it saves energy effectively. The disadvantage is that the SPIN broadcast mechanism cannot guarantee the reliable transmission of data. When all neighboring nodes of the node that generated or received the data do not need the data, the data cannot be forwarded further, so that the remote node cannot get the data; and When a sink needs any data, the energy of its surrounding nodes is easily exhausted. Figure 1 shows the routing establishment and data transmission of the SPIN protocol.

Figure 1 SPIN protocol road curve establishment and data transmission
③Directed diffusion (DD) protocol: DD protocol names the data it generates with a set of attribute values. To establish routing, sink nodes flood Interest messages containing query tasks in the entire network or part of the area; nodes along the way cache and merge each Interest as needed, and calculate and create data containing information reporting rate, next hop, etc. according to Interest Gradient (gradient), thus creating multiple paths to the sink point. The nodes in the geographic area of ​​Interest start monitoring tasks as required and report data periodically. Each node on the way can cache and aggregate the data; sink points can be transmitted through a certain path during the data transmission. The reporting interval is smaller Or a larger Interest to increase or decrease the data reporting rate. The advantages of the protocol are: multi-pathing and good robustness; the use of data aggregation reduces data traffic; the sink point uses enhanced or weakened methods to effectively use energy according to the actual situation; the use of query-driven mechanism to establish routes as needed, avoiding the preservation Web information. The disadvantages are: it is not suitable for applications such as environmental monitoring; the gradient overhead is very large, and it is not suitable for multi-sink network; the data aggregation adopts time synchronization technology, which brings greater overhead and delay. Figure 2 shows the route establishment process of Directed Diffusion protocol.
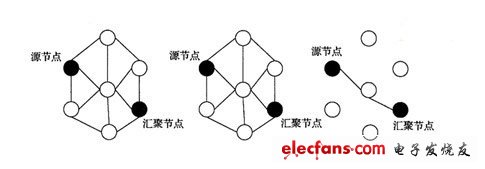
Figure 2 Directed Diffusion protocol routing process
â‘£Rumor protocol: Rumor protocol attracts unicast random forwarding of query messages. When a node detects an event, it saves it, and creates a data packet called an agent with a long life cycle that includes information about the event and the source node. It forwards it on the network according to one or more random paths and receives The agent's node establishes a reverse path based on the event and source node information, and sends the agent to the neighboring node again randomly, and can add its known event information to the agent before sending it again. At the same time, the query request of the sink node is also forwarded along a random path, and the route is established when the two paths cross; if they do not cross, the sink point can flood the query request. The advantage of this protocol is: it is suitable for the situation of multiple sinks, a large number of query requests, and few network events. The disadvantage is that if there are too many events, the overhead of maintaining the event table and sending and receiving agents will be very large; and because the Rumor protocol uses a random way to generate the path, the data transmission path is not optimal, and there may even be routing loop problems. Figure 3 shows the intersection of Agent path and query path in Rumor protocol.

Figure 3 Schematic diagram of rumored routing
Introduction
SCOTECH manufactures a full range of three phase distribution transformers, they can be oil immersed or dry type, equipped with or without oil conservator, hermetically sealed or free breathing, with corrugated tank or equipped with radiators. The three phase Distribution Transformer are widely used in power system.
Scope of supply
Primary voltage up to 35KV
Rated power: small size up to 315KVA, medium size up to 2500KVA, large size up to 25MVA
Installation: free standing, pole mounted, pad mounted type
Standards
SCOTECH`s three phase distribution transformers are designed and manufactured in accordance with all major international standards (IEC, ANSI, UL, etc.)
Why SCOTECH
Long history- Focus on transformer manufacturing since 1934.
Technical support – 134 engineers stand by for you 24/7.
Manufacturing-advanced production and testing equipment, strict QA system.
Perfect service-The complete customer service package (from quotation to energization).
Three Phase Distribution Transformer
3 Phase Transformer,Three Phase Transformer,Three Phase Distribution Transformer,Three Phase Pole Mounted Transformer
Jiangshan Scotech Electrical Co.,Ltd , https://www.scotech.com