SSDs offer a key configuration choice in the Windows Device Manager, and different settings can significantly impact performance. Many users might not be aware of how these options affect their system. Today, we're going to explore how optimizing SSD settings can improve your experience. This topic came up in discussions with some readers, so let's dive into what happens when you adjust these settings.

To start, open the Device Manager by pressing Win + X and selecting "Device Manager." Locate your SSD under the "Disk drives" section, then double-click it. Switch to the "Policy" tab, where you'll find the "Enable Write Caching on the Device" option. This setting determines whether data is written to the cache first or directly to the NAND flash memory. The difference this makes can be quite significant, especially in terms of speed and responsiveness.
When you enable the write cache, the SSD writes data to the cache first, which allows the system to acknowledge the write operation faster. This results in better performance, particularly in tasks involving smaller file sizes like 4K or 64K operations. However, there's another option called "Turn off Windows Write Cache Buffer Refresh," which can further enhance performance.
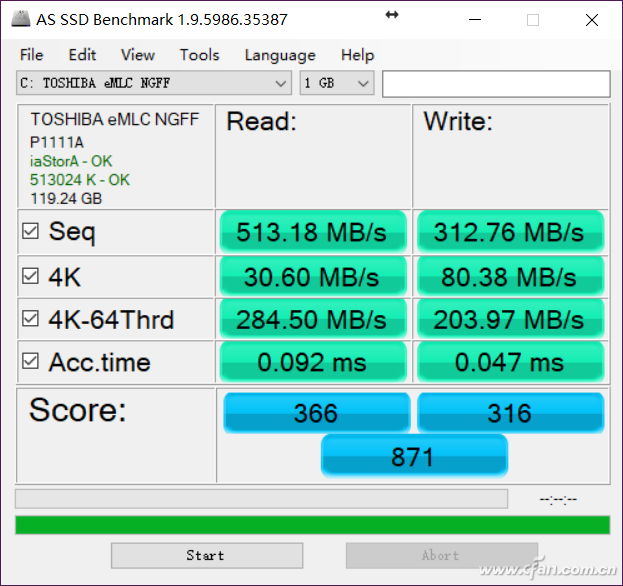
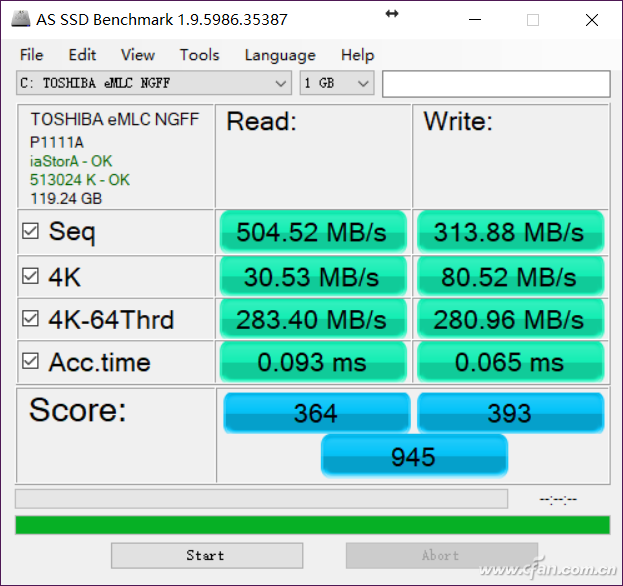
Enabling this option changes the disk cache policy to "write back," meaning the system assumes the data is safely stored in the cache without waiting for it to be fully written to the drive. This can boost performance, but it also introduces risks—like data loss during unexpected power outages. If you disable this feature, the cache policy shifts to "read ahead," which preloads data based on system behavior, improving read speeds in certain scenarios.
One thing to note is that testing software often doesn't reflect the full benefits of the "read ahead" strategy. That's because such optimizations are handled at a lower level (Ring 0) in Windows, while most testing tools operate at Ring 3. Additionally, read-ahead relies on the system predicting what files you'll need next, which isn't always accurate during benchmarking runs.
If you disable the write cache entirely, you'll notice a sharp drop in performance. In this case, all write operations must wait until the data is actually written to the NAND flash, which slows down the process significantly. This is why it's generally recommended to keep the write cache enabled unless you're concerned about data integrity in unstable environments.
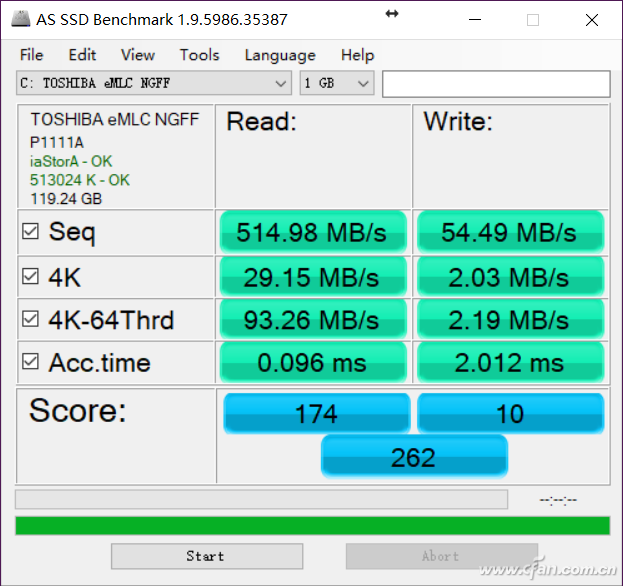
In summary, the write cache plays a crucial role in SSD performance. Enabling it can lead to noticeable improvements, especially in everyday tasks. However, be cautious with the "Turn off Windows Write Cache Buffer Refresh" option. While it enhances performance, it increases the risk of data loss if the system crashes or loses power unexpectedly.

Cooling Coating For Electrical Equipment,Cooling Coating For Petrochemical Industry,Cooling Coating For Grain Storage,Cooling Coating For Logistics Industry
ZHONG HAN INTERNATIONAL TRADE CO., LTD , https://www.cck-ht.com