With the environmental awareness in the field of indoor navigation, logistics management, control access, real-time monitoring and other fields. The research on indoor location sensing system and wireless network positioning has attracted much attention, and research topics on RFID (Radio Frequency IdenTIficaTIon, RFID) positioning technology have begun to appear. RFID tag-based positioning technology follows the basic principle of wireless positioning. Considering the particularity and limitation of RFID technology, future positioning methods should focus on RF transmission models, reader diversity and scalability. This paper summarizes the existing RFID positioning technology, introduces the positioning principle widely used in modern indoor wireless networks, and classifies the main RFID positioning schemes.
1 RFlD technology
RFID is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically identifies target objects and acquires relevant data through radio frequency signals. The RFID system is mainly composed of: a tag, a reader/writer and a database management unit, as shown in Fig. 1.
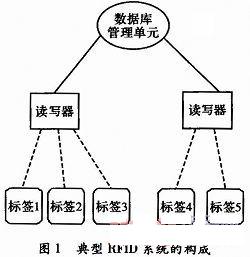
The working principle is that after the tag enters the magnetic field, it receives the radio frequency signal emitted by the reader, and the information obtained by the induced current emits the information stored on the chip; or actively sends out the signal of a certain frequency. After reading and decoding the information, the reader sends it to the data management system for data processing.
RFID tags can be divided into two types: active electronic tags, the working power of the tag is completely supplied by the internal battery, and the energy supply of the tag battery is also partially converted into the RF energy required for the electronic tag to communicate with the reader. The passive electronic tag does not have a built-in battery. When the reader is out of the reading range, the electronic tag is in a passive state. When the reader is within the read range of the reader, the tag is extracted from the RF energy emitted by the reader. The power required for its work. Passive electronic tags are small in size and low in cost, but they are inferior to active electronic tags in terms of reading and writing distance and adapting to object motion.
The RFID reader is composed of an antenna, a radio frequency transceiver module, a signal processing unit, a control unit, and an interface circuit. The RF transceiver module completes RF signal reception, transmission, modulation and demodulation, and power control; the main functions of the signal processing unit are anti-collision algorithm implementation and information encryption, decryption, verification, and error correction; the control unit coordinates the operation of the entire reader. The interface circuit completes the data transfer between the reader and the data management system.
The data management system stores and manages the data by the database. It communicates with the RFID readers distributed everywhere through various interfaces to obtain the tag information captured by the RFID reader in real time.
2 indoor wireless network positioning principle
The propagation of wireless signals in indoor environments is often affected by multipath, non-line of sight, diffraction and reflection, so that the proposed indoor positioning algorithm cannot accurately measure signals. Positioning algorithms can be classified into distance estimation methods, scene analysis methods, and proximity methods.
Zinc Wire is a good anti-corrosion material,widely used in steel structure anti-corrosion,wind power tower,bridge,sluice gate,oil pipe on sea,Ductile Iron Pipe,extrusion division tube.
|
|
Zinc Wire
Zinc Wire,High Pure Zinc Wire,Zinc Wire Mesh,Corrosion Protection Zinc Wire
Shaoxing Tianlong Tin Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.tianlongspray.com